Project: GitLab
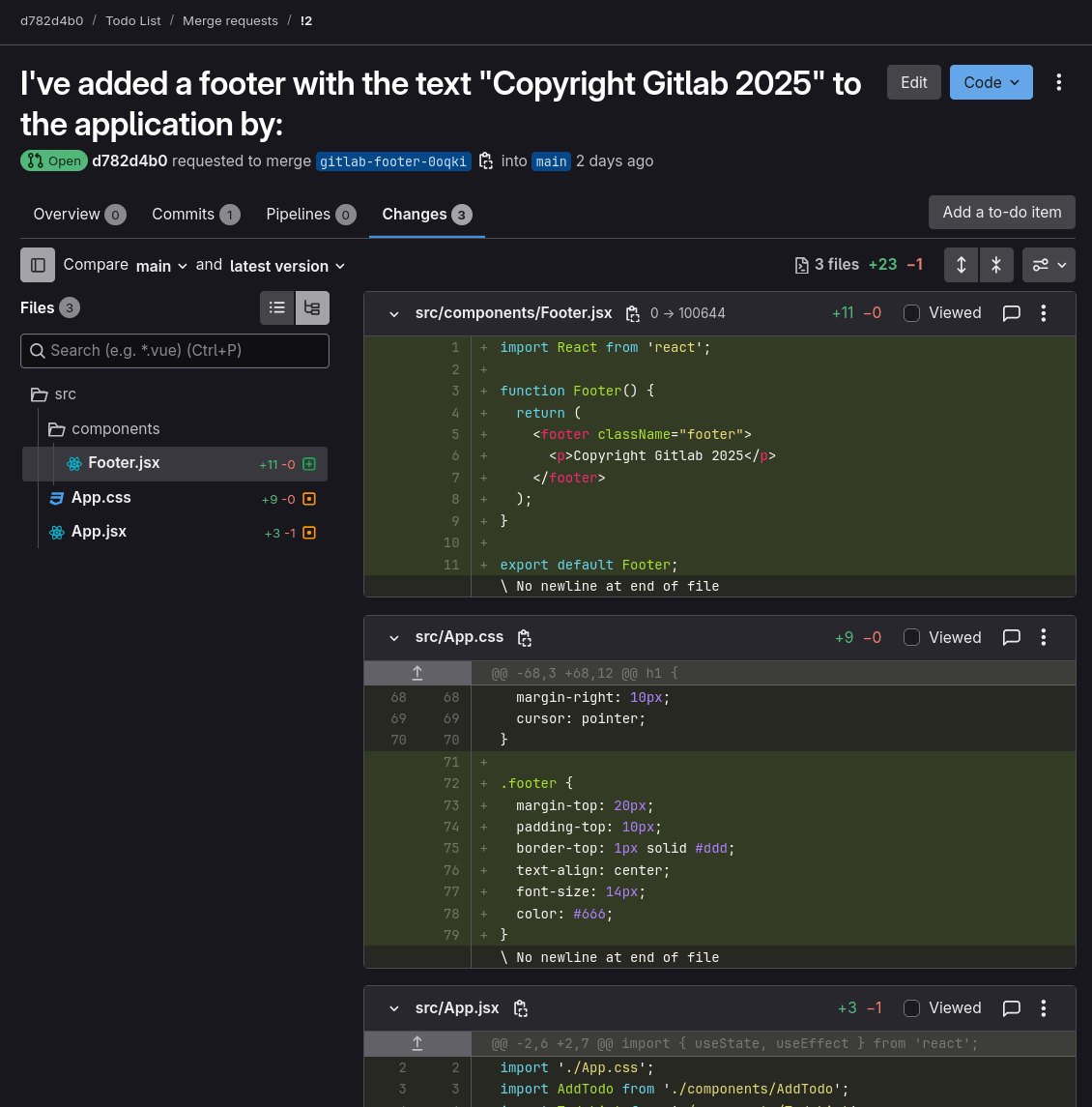

AI PR Agent
GitLab
An AI-powered tool that enables developers to create or update pull requests through natural language prompts, analyzing codebases and making appropriate changes automatically.
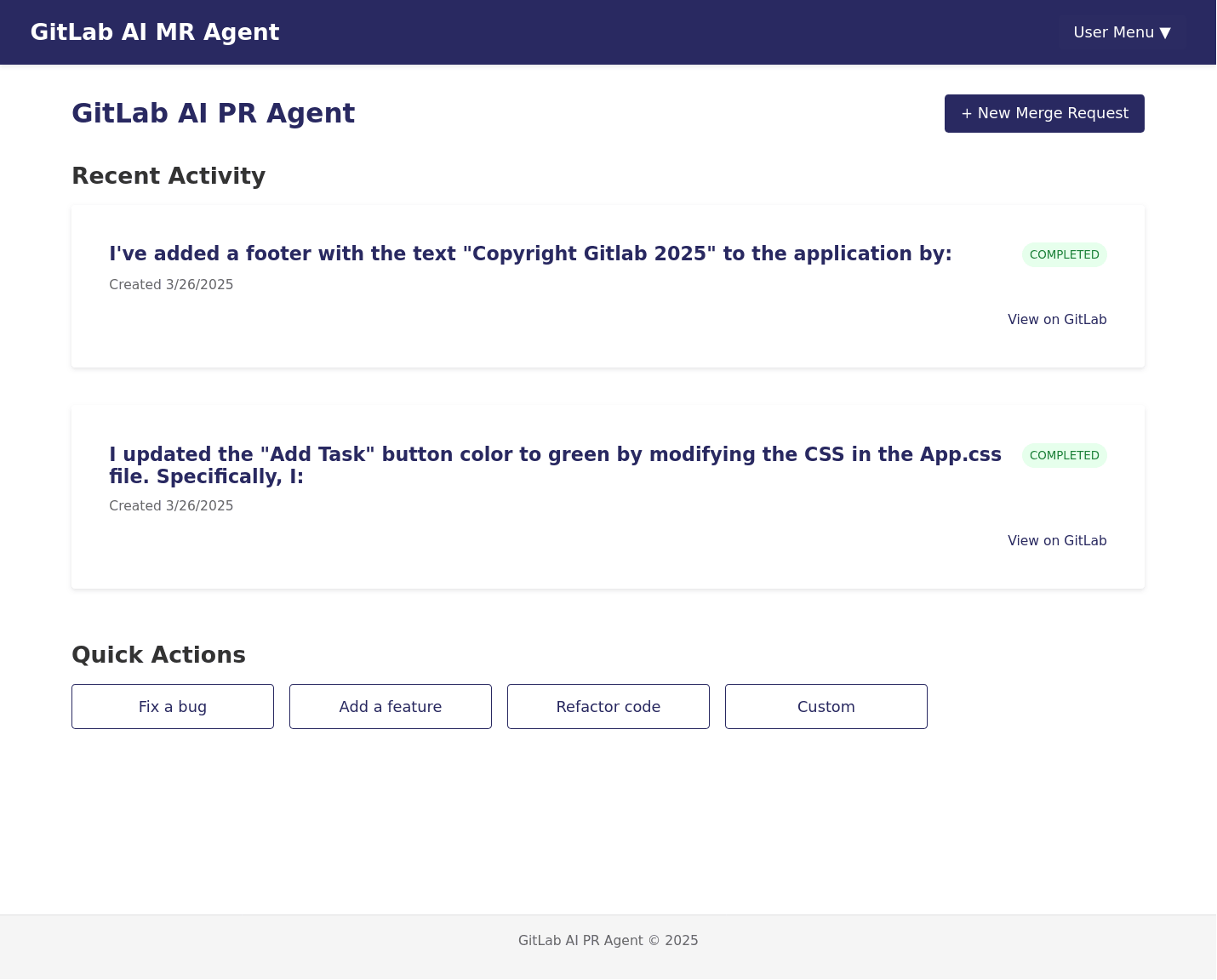
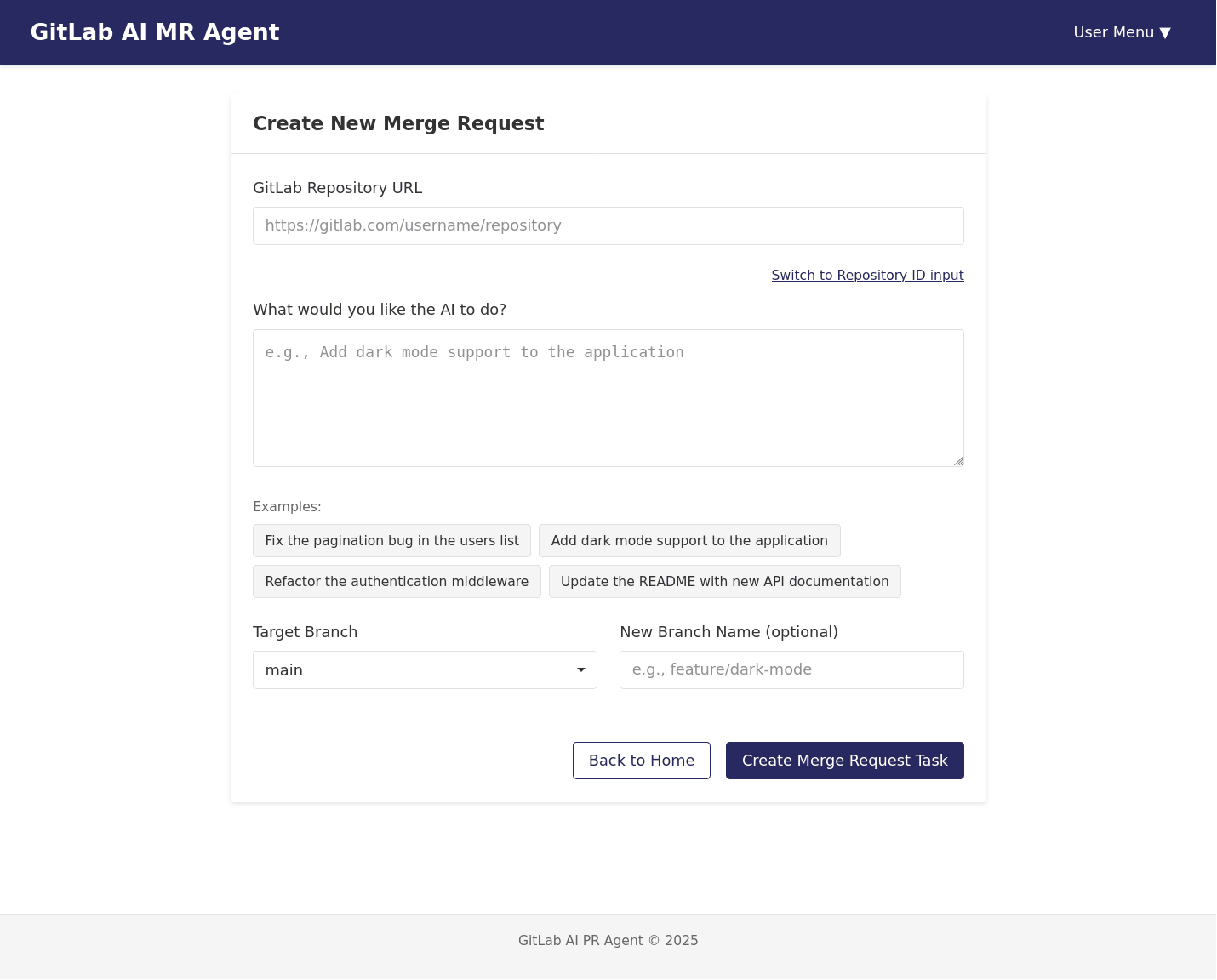
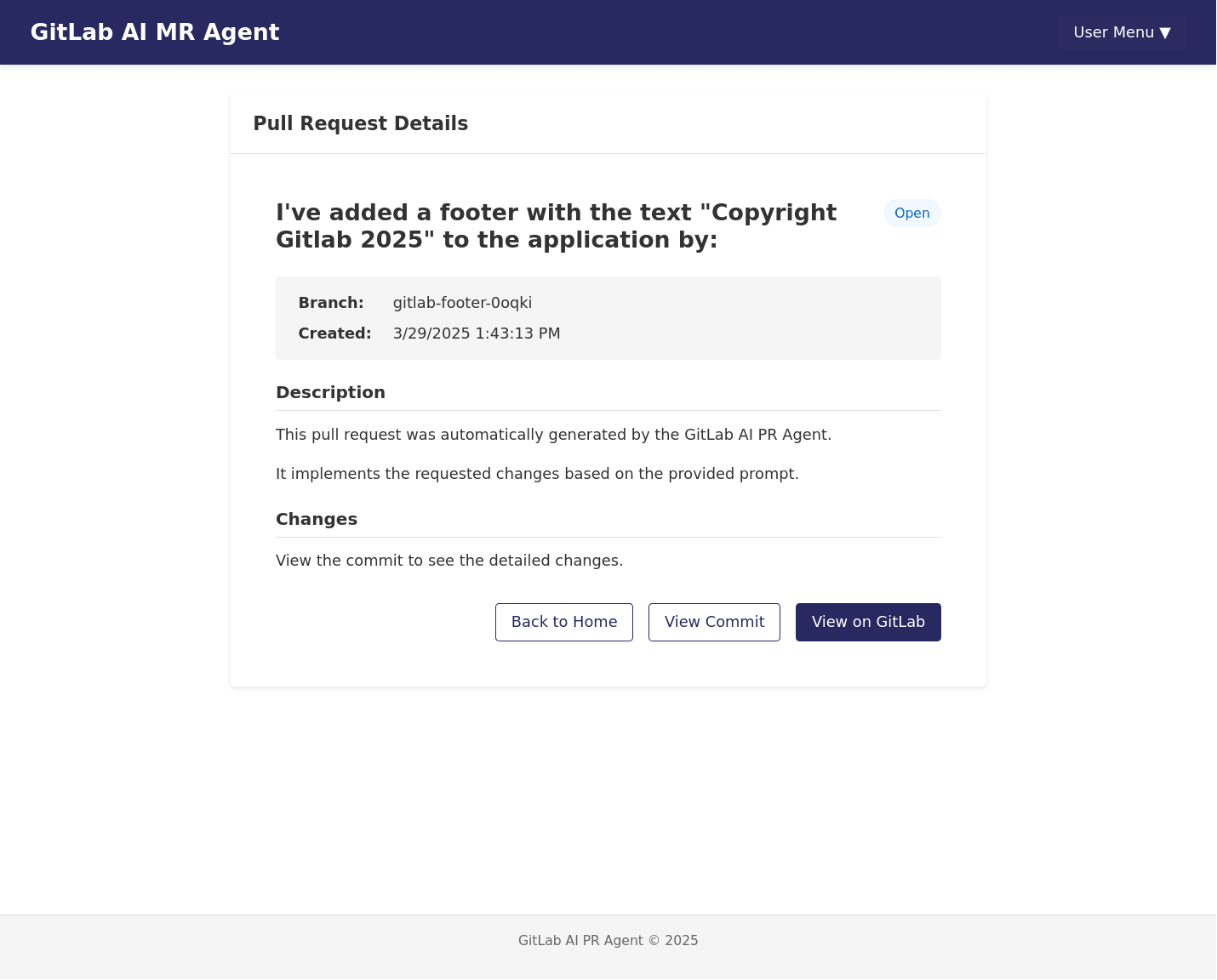
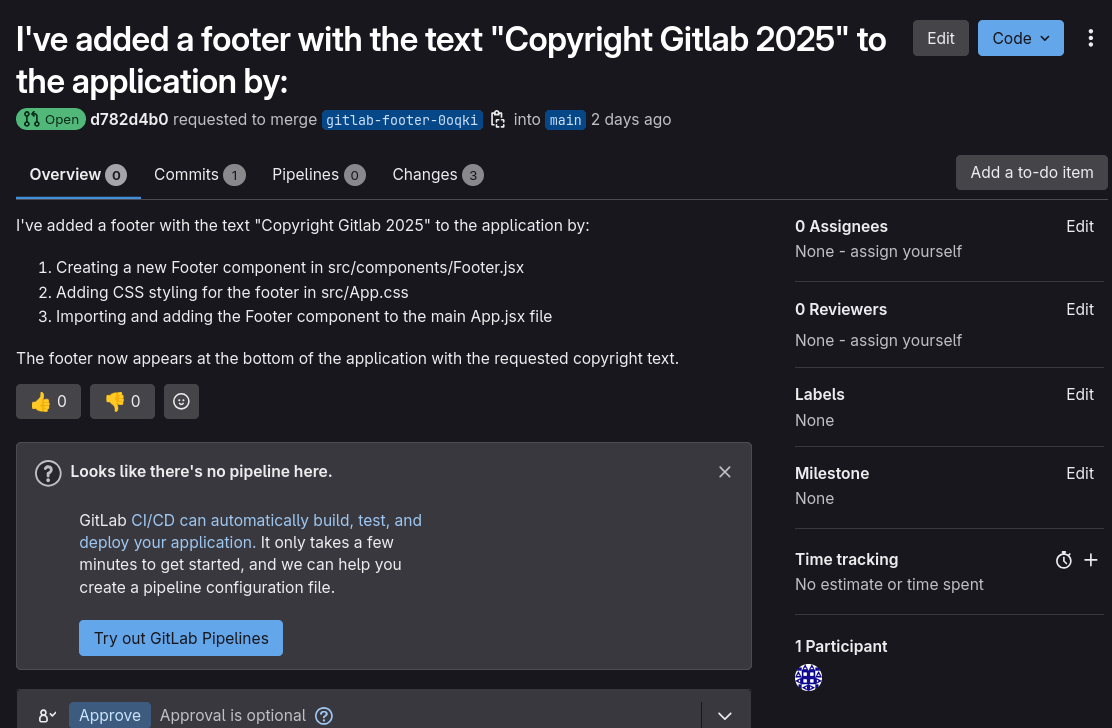
Project Demo
Project Metrics
Project Details
The AI PR Agent demonstrates expertise in distributed systems, cloud architecture, and AI integration for a GitLab Principal Engineer position by creating an autonomous PR creation system. It allows developers to describe changes in natural language and the system translates these into actual code changes.
Business Value
- Developer Productivity
- Workflow Automation
Key Features
Natural Language PR Creation
Users can describe desired changes in plain English, and the system translates these into actual code changes.
Autonomous Code Analysis
The system uses Claude 3.7 to analyze repositories, understand code structure, and generate appropriate changes.
GitLab Integration
Seamless integration with GitLab's API for creating branches, committing changes, and opening pull requests.
Tool-based AI Approach
The Claude client uses a tool-based approach where the AI can use various tools to interact with the repository, such as listing files, reading file contents, writing to files, and searching for patterns in code.
Technologies Used
Frontend
Backend
DevOps
Other
Challenges & Solutions
Autonomous Code Analysis
Implemented a tool-based approach where Claude can use various tools to interact with the repository, allowing it to explore the codebase autonomously and make informed decisions about code changes.
Asynchronous Job Processing
Designed a job system with DynamoDB for persistence and Lambda functions for processing, with a defined lifecycle and detailed status updates for tracking progress.
Managing Claude Context Window
Implemented a strategy to selectively include relevant code files in the Claude context, using code search and analysis to identify the most important files for a given task.
Key Learnings
- AI Tool Design: Designing effective AI tools requires careful consideration of the interaction model. The tool-based approach proved effective for giving Claude the ability to explore and modify code repositories autonomously.
- Asynchronous Architecture: Long-running AI tasks benefit from an asynchronous architecture with proper status tracking and updates, providing a better user experience and more efficient resource utilization.
- Type Safety: End-to-end type safety with TypeScript and Zod significantly improved development velocity and reduced runtime errors, especially when working with complex data structures and API interactions.
- Meeting Users Where They Are: Integrating directly with existing tools like GitLab proved valuable, allowing users to work within familiar interfaces rather than forcing them into a new environment.